
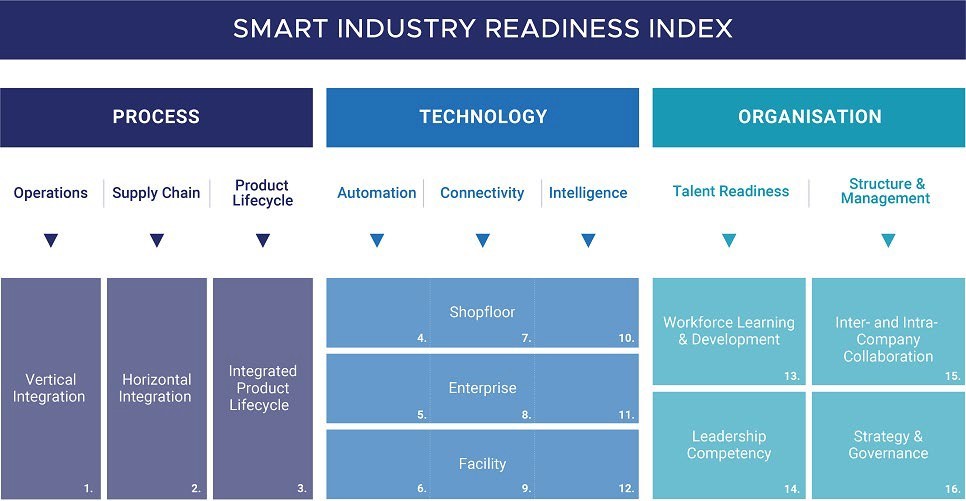
Leveraging Smart Industry Readiness Index (SIRI) for knowledge management blueprint and organisation transformation
Introduction
In today’s dynamic and competitive business environment, organizations recognize the critical importance of knowledge management (KM) in achieving sustainable growth and maintaining a competitive edge. KM involves the systematic management of an organization’s knowledge assets to create value, foster innovation, and improve decision-making processes. It encompasses four key components: people, processes, technology, and strategy. By effectively managing these components, organizations can leverage their intellectual capital to drive innovation, enhance operational efficiency, and achieve strategic objectives.
History and adoption of Smart Industry Readiness Index
The Smart Industry Readiness Index (SIRI) was developed by the Singapore Economic Development Board (EDB) in collaboration with industry partners. It was conceived as a response to the rapid advancements in Industry 4.0 technologies and the need for organizations to assess their readiness to adopt these technologies effectively. (https://www.tuvsud.com/en-sg/resource-centre/stories/smart-industry-readiness-index). It addresses dimensions that match the focus of the capitals. The financial capital is tagged to the technology dimensions, the structural capital to the process dimensions and the talent capital with the organisation capital.
Since its inception, Smart Industry Readiness Index has been championed by the Singapore EDB and has gained significant traction among companies in Singapore. The EDB has actively promoted Smart Industry Readiness Index as a tool for assessing and enhancing the Industry 4.0 readiness of companies across various sectors. It has provided guidance and support to companies in implementing Smart Industry Readiness Index assessments and leveraging the results to drive digital transformation initiatives.
To date, Smart Industry Readiness Index has been deployed by numerous companies in Singapore and internationally, helping them evaluate their readiness across people, processes, and technology dimensions and identify areas for improvement to remain competitive in the global market.
Smart Industry Readiness Index as a KM tool
The first step in implementing knowledge management through Smart Industry Readiness Index involves utilizing the index to assess the organization’s readiness across the people, process, technology, and strategy dimensions.
The people dimension evaluates the organization’s human capital readiness, including skills, competencies, and culture necessary for knowledge sharing and collaboration. Through Smart Industry Readiness Index assessments, organizations can identify strengths and areas for improvement in employee capabilities, leadership support for knowledge initiatives, and the overall knowledge-sharing culture within the organization.
The process dimension examines the organization’s operational workflows, policies, and procedures to assess their alignment with knowledge management objectives. Smart Industry Readiness Index helps identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for streamlining processes to facilitate knowledge creation, capture, dissemination, and utilization across the organization.
Technology readiness assesses the organization’s infrastructure, systems, and tools supporting knowledge management activities. Smart Industry Readiness Index enables organizations to evaluate their technological capabilities in terms of data analytics, collaboration platforms, knowledge repositories, and other digital solutions essential for effective knowledge management.
The strategy component involves the development of a clear vision and roadmap for knowledge management aligned with the organization’s overall goals and objectives. Smart Industry Readiness Index assessments help organizations identify strategic gaps and opportunities, enabling them to formulate robust KM strategies that drive organizational success.
Creating the organization knowledge management blueprint
Based on the assessments conducted through Smart Industry Readiness Index, organizations can develop a comprehensive knowledge blueprint that outlines the strategic priorities and action plans for implementing knowledge management initiatives. The knowledge Management blueprint integrates findings from the Smart Industry Readiness Index assessments and aligns them with the organization’s overarching goals and objectives.
The knowledge management blueprint prioritizes areas for intervention based on the findings from Smart Industry Readiness Index assessments and the organization’s strategic imperatives. A prioritisation matrix is developed, weighting the components of people, process, technology, and strategy according to their importance in driving knowledge management effectiveness.
With the blueprint in place, organizations can deploy targeted knowledge management strategies tailored to address specific gaps and opportunities identified through the SIRI assessments. These strategies may include training and development programs to enhance employee skills, redesigning processes to facilitate knowledge flow, implementing technology solutions to support knowledge sharing and collaboration, and aligning KM initiatives with overarching organizational strategies.
Implementation of Smart Industry Readiness Index as a tool for knowledge management gaps, insights and elicitation in the School of Engineering
Using the Smart Industry Readiness Index to assess the people, process, and technology indexes involve a structured approach that engages multiple levels of the school. Here’s a brief sharing on how Smart Industry Readiness Index was utilized as a tool to KM gaps, insights and elicitation for the School of Engineering at Institute of Technical Education, College Central, Singapore.
The implementation begins by familiarizing the school’s leadership with the Smart Industry Readiness Index framework and its objectives. This was followed by the formulation of a plan to conduct Smart Industry Readiness Index assessments across different departments of the school, including management and operational employees.
The Smart Industry Readiness Index assessment starts by engaging senior leadership and management teams in the Smart Industry Readiness Index assessment process. This involves evaluating the school’s strategic direction, leadership support for initiatives, and overall alignment with Industry 4.0 principles and organisation goals.
Next comes the involvement of middle management in the assessment to gauge their understanding of digital technologies, their ability to drive change, and their role in fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration.
Finally, operational employees are included in the assessment to capture their perspectives on technology adoption, process efficiency, and opportunities for improvement in day-to-day operations.
Once the assessments are completed, data collected from each department was used to map the assessment results into radar graphs, with the people, process, and technology indexes represented on different axes. The radar graphs provide a visual representation of the department’s readiness across these dimensions, highlighting areas of strength and improvement.
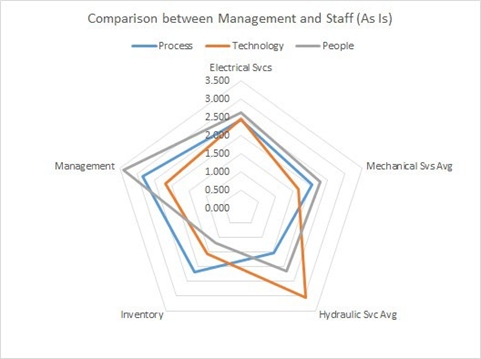
The radar graphs are then analysed to identify gaps and discrepancies between departments. Patterns or trends that indicate common challenges or areas of opportunity related to knowledge management are identified. A point to take note is to pay particular attention to areas where there is a significant disparity between management’s perception and operational realities, as these may signify potential communication or alignment issues.
Based on the insights gained from the Smart Industry Readiness Index assessments and radar graph analysis, the school proceeds to develop a comprehensive KM blueprint. Prioritize areas for intervention, focusing on bridging the identified gaps and aligning organizational to school capabilities with strategic objectives.
Smart Industry Readiness Index findings regarding people-related KM gaps, such as skill deficiencies or knowledge-sharing culture issues, are translated into learning and training plans. These plans include professional development workshops, seminars, online courses, and mentorship programs aimed at enhancing staff capabilities in relevant areas. By investing in staff training and development, the school cultivates a culture of continuous learning and knowledge sharing among its personnel.
Process-related KM gaps identified through Smart Industry Readiness Index assessments are documented and addressed through the implementation of standard operating procedures (SOPs) or policies. SOPs and policies serve as guidelines for streamlining workflows, improving efficiency, and ensuring consistency in operations. By documenting and formalizing processes, the school minimizes errors, reduces inefficiencies, and promotes best practices in knowledge management.
KM insights related to technology utilization are incorporated into the operation and training facilities of the school. This may involve upgrading or implementing new technologies that facilitate knowledge sharing, collaboration, and information management. By integrating technology into daily operations and training activities, the school enhances its capacity to capture, store, and disseminate knowledge effectively.
KM is sharpened through daily improvisation and improvement, with staff encouraged to identify opportunities for enhancing knowledge management practices. Feedback mechanisms, such as suggestion boxes, surveys, or regular meetings, enable staff to contribute ideas for improving KM processes and systems. The school fosters a culture of innovation and adaptability, where continuous improvement is embraced as a core value.
Annually, the school conducts a mid-year review of its KM operation to assess progress, identify any remaining gaps, and uncover new KM opportunities. Smart Industry Readiness Index is deployed again during this review process to re-evaluate the school’s readiness across people, processes, and technology dimensions. Based on the review findings, adjustments are made to the KM strategy and action plans to ensure alignment with evolving organizational needs and goals.
By systematically integrating Smart Industry Readiness Index findings into its operation management structure and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, the school ensures that KM remains a cornerstone of its strategy, driving excellence in teaching, learning, and overall school performance.
By leveraging Smart Industry Readiness Index insights through KM, organizations can not only address knowledge gaps but also implement transformative technologies like digital twinning to drive innovation, agility, and competitiveness in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape.
Some outcomes of the KM include the school building capabilities in digital twinning.

KM insights on different learning abilities of inclusive workers lead to new learning approaches and digital tools. One such innovation is using mixed reality for worker’s reinforced and 24/7 learning.

Another KM insights on the need to respond to higher customer service and support level resulted in the Web 3.0 implementation of Product as a Service. Students can now have democratized service support learning anywhere globally through digital engagement with tools such as Real-Wear and Microsoft Teams.

Conclusion
Smart Industry Readiness Index assessments serve as a foundation for developing and prioritizing KM strategies aimed at addressing identified gaps and opportunities. By integrating Smart Industry Readiness Index findings with KM initiatives, organizations can ensure alignment between knowledge management efforts and broader organizational goals. In recognition of its significance, Smart Industry Readiness Index was featured in the World Economic Forum’s (WEF) Advanced Manufacturing and Production Industry Community. This platform has provided Smart Industry Readiness Index with increased visibility and credibility on the global stage, positioning it as a benchmark for assessing Industry 4.0 readiness worldwide. By identifying organization industry readiness indices across people, process, technology, and strategy dimensions, Smart Industry Readiness Index facilitates the creation of a comprehensive knowledge blueprint that guides the deployment of knowledge management strategies. Through this integrated approach, organizations can harness their intellectual capital more effectively, driving innovation, competitiveness, and sustainable growth in the digital age.
Header image source: World Economic Forum, CC BY-NC-ND 4.0.






