AI-based KM features for knowledge retention and reuse [Generative AI & KM series part 4]
This article is part 4 of the series AI integration strategy for learning and knowledge management solutions.
A comparative study of 100 generative AI tools in the context of learning and knowledge management (KM) was conducted and has resulted in a set of 35 KM processes where generative AI1 has augmented their experience, implementation, and execution. This article (part 4 in the series) focuses on knowledge retention and reuse KM processes.
Part 4. Knowledge retention & reuse
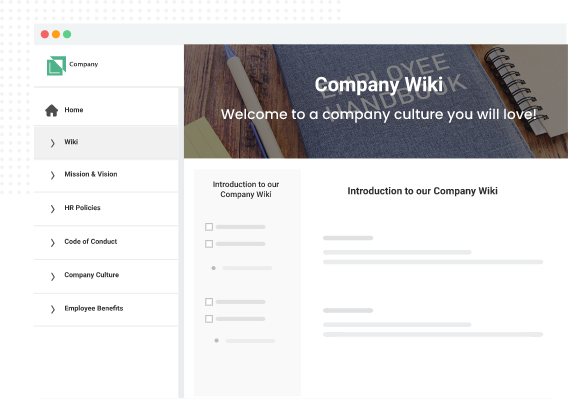
4.1. Assist in creating rich content (wiki, KB, reports)
With the help of generative AI, creating content and summarizing complex topics can be facilitated and semi-automated. AI algorithms can help in the writing of domain-specific reports (i.e.: financial), removing the risk of error in manual writing to ensure accuracy, consistency, and compliance. AI can enable shared content creation and editorial workflow that enables cost-effective management. For example, it can auto-fill templates for consistent content that’s easier for employees to edit and complete later on. Another AI feature would be “write it with me” – An idea auto completion that generate and complement an idea with supporting argument and examples. For example, a customer call agent would get assistance on creating a robust ticket response with one click based on just a few words typed.

AI can play the role of article planner – ability to plan for new and/or missing support articles based on the history of customer conversations or community discussions. AI can also generate articles from audio & video files making them editable, searchable, and collaborative, later they can be imported into the company knowledge base for future reference and reuse.
4.2. Feedback loops and lessons learned
With the help of generative AI, it is possible to collect relevant input and reactions early in feedback review process. These inputs and reactions provide information that allows mitigation of expensive mistakes later in the process, as well as finding new ways of solving problems. This is often tricky as it might impact who needs to get involved in the work. It has more characteristics of designing a stakeholder map than just studying behavior and data. AI algorithms can help in the identification of relevant stakeholders for review and to collect early feedback in the process. It can also help in clustering similar feedback into groups and themes, making sense of them for improved process design, re-engineering and decision making.
4.3. Content syndication & inline integration
Community content syndication refers to the ability to automatically transfer and deploy content anywhere: websites, intranet, or client collaboration platforms. With the help of generative AI, the community content can be inline integrated with virtual case management, ticketing system or any organizational systems. For example, FAQs from community forums can be embedded into self-service customer portals. AI algorithms can develop the connected Knowledge capability empowering knowledge seekers to find the answers they need directly in their line of sight while handling their job tasks.
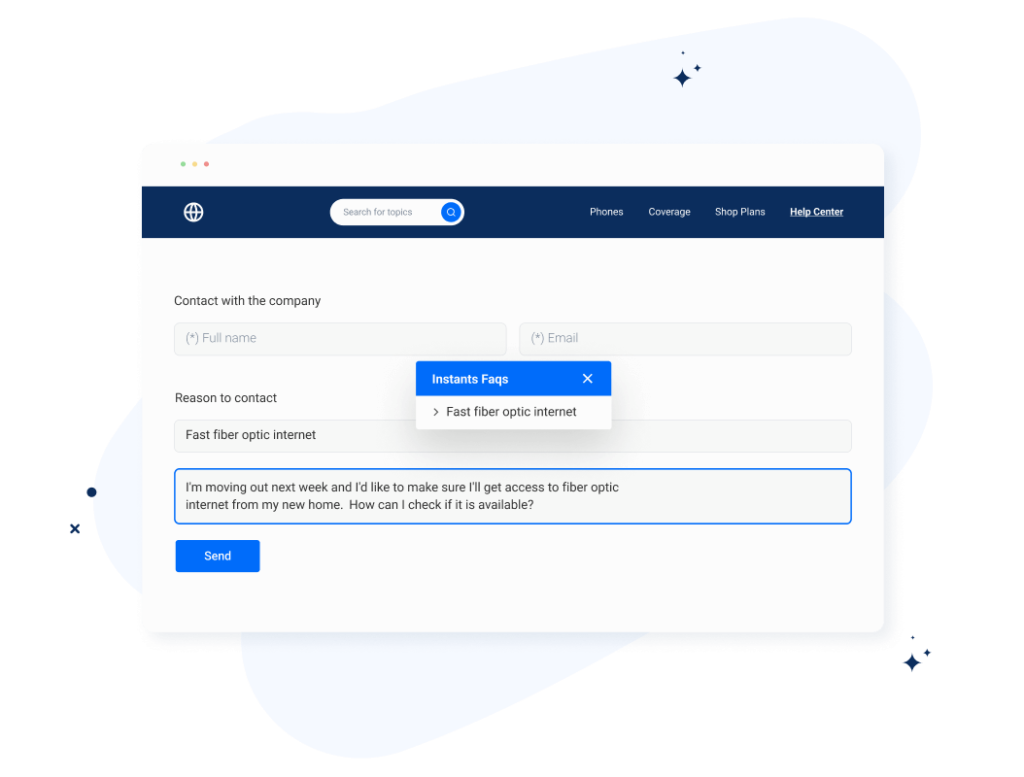
For example, a customer call agent can directly consult the community resolved cases within his/her customer call or webchat system. The customer call agent may improve his/her first contact resolution by mirroring and co-browsing content from different communities and data sources without the need to interrupt the flow of work.
4.4. Insights and best/direct answers extraction
With the help of generative AI, employees can gain insights from pattern analysis or perform root cause analysis on a specific issue for an informed decision making. For example, “I want to uncover insights about the decreasing sales of product A”. Research scientists can aggregate information from millions of scientific documents and news releases, providing them with an efficient, one-stop shop where they can discover insights that drive their research. AI can also help product managers generate insights from product comparisons, brand community discussions, up-to-date, accurate financial data, and approved content.
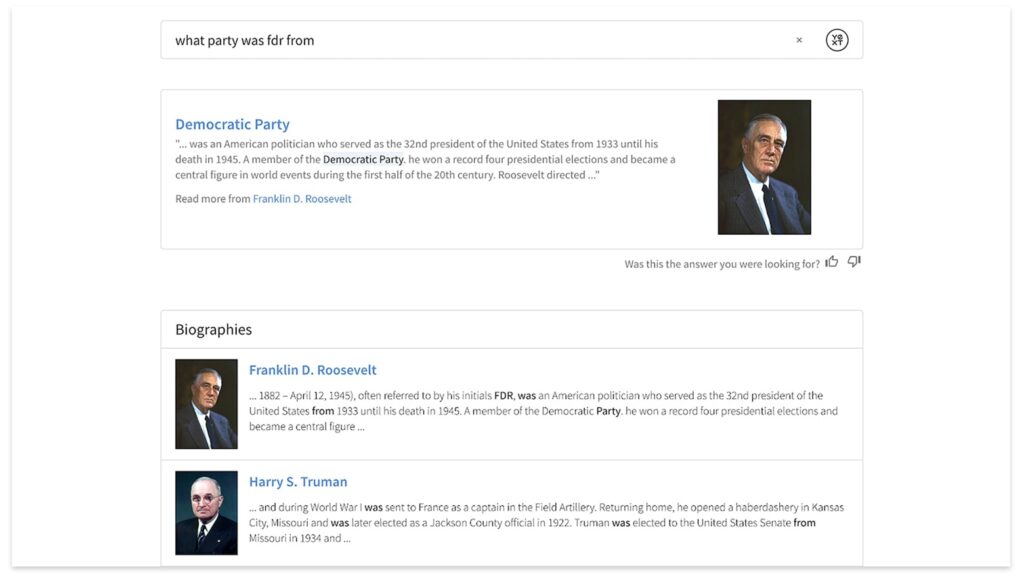
AI can also provide direct answers using an extractive question-answering (QA) system. In extractive QA, a specially trained version of BERT (Google’s open-source neural network which is trained to understand language) helps to identify the excerpts from long documents that best answer the user’s question. If it finds a good answer in the text, the algorithm displays it as a featured snippet. These snippets provide a great search experience and help searchers find the best answers to their queries, in a focused in-line section. AI algorithms require guidance and supervision to define which information and data are most important to the managers to lay down the foundation for meaningful insights and best direct answers.
4.5. Knowledge portal: diffusion of reusable content
With the help of generative AI, knowledge portal / homepage can be drafted with initial layout and structure to curate content, blogs, newsletter, events, RSS feeds, or any topic of interest. Knowledge portals centralize access to knowledge resources from various repositories and personalize the experience for each department and team. For example, AI algorithms can help in drafting self-service portals for HR and IT knowledge, so employees can access enterprise-wide content in one place. AI can also draft a homepage for every employee, so important announcements and real time updates on topics of interest are personalized with AI-suggested content for each user. All relevant interactions are available in one view, with the ability to customize and brand portals for internal teams as well as external customers.
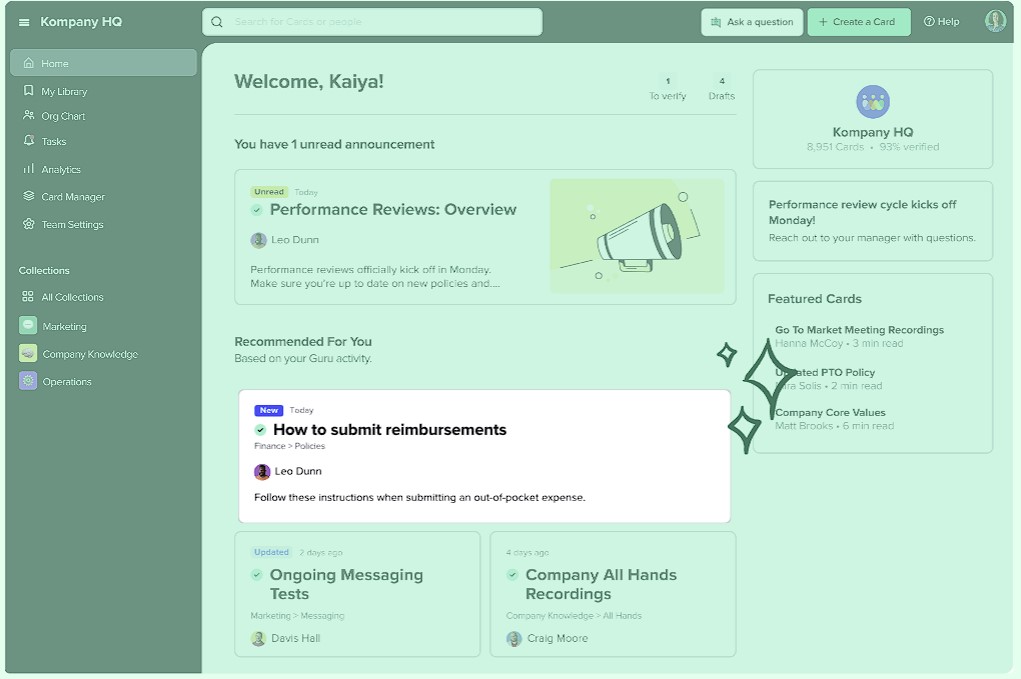
Examples of AI-based KM tools for knowledge retention and reuse: RightAnswers, Guru, Kyndi, InBenta, Yext, Textio.
Next part (part 5): AI-based KM features for expertise discovery and dissemination.
Header image source: Author provided.
Reference:
- Najjar, R. (2023, July 13). Preliminary Understanding of Generative AI: What & How? Medium. ↩






